How to... do a SWOT analysis
As part of a job interview process, you might be asked to do a SWOT analysis. Not sure where to start? Read on!
Managerial candidates may be asked to complete a SWOT on one of a range of topics, to demonstrate their industry knowledge. Topics to be looked at often include;
- Self-facing (Candidate)
- Potential employer (specific retail/healthcare location or wider business)
- Potential employer competitor (as above)
How To Do: SWOT Analysis
A SWOT Analysis is a tool that is used to analyse an individual, location, brand or business’s situation and does this by breaking it down into four different sections which review the subject's Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats.
Typically a SWOT will be built on the knowledge/insight gained during a mystery shop. You should of course be covert and also respectful during a mystery shop. Whilst directly engaging with an employer about your purpose might sound sensible, it may reveal that a process is going on that they were previously unaware of!

Initially, the layout is straightforward, whether you are handwriting, writing a Word document or even producing a PowerPoint, ultimately there will be 4 headers - the 4 elements of SWOT.
The first section focuses on the topic's internal Strengths that they can manage. This is the section that allows you to identify what they do well and perhaps is different in comparison to their competitors; what gives them that edge? Your first initial strengths will be some of the most important due to this also being what the customers will spot straight away. However, once you have seen through the initial strengths you then get the opportunity to dig deeper to find out what else they do well. Things such as food quality, customer service, prices, staff appearance or business merchandising standards.
The second section focuses on the topics internal Weaknesses that they can manage, control and change. This section allows you to identify areas of the business which aren’t doing so well but that the business is in control of and could change. These are the topic's weaker points which could be based on customer service skills, cleaning skills or things such as merchandising standards.
The third section focuses on the subject's external Opportunities. This is where you need to think outside of the box and examine what potential opportunities there are to grow, improve etc. Examples of what chances you think the business can/should take or changes the business may have to make to be able to improve, compete or simply survive in a very difficult economic climate. This is where you take external factors such as their competitors, market trends and business events and use them to the business's advantage by trying to replicate what success looks like to that business specifically to make a positive change.
The final section focuses on the business's external Threats. In this part of the SWOT, you must analyse what threats can oppose the business. Threats can include new Laws and Regulations, business competition, new business openings (the Internet!) and upcoming market trends. Analysing these is important to the business as it helps the business to get in front of the threats before they start to damage the business.
Overall, the Swot analysis is used to review an individual or business's performance and help them to get in front of any potential problems. Businesses like to get their potential employees to complete these as it helps them to see their business from a different perspective, we ask our candidates to be constructive and positive with any recommendations that come from a SWOT analysis; a PowerPoint presentation or even some notes on a page; the SWOT analysis is about the quality of the content and delivering the message in a positive way. Even if you are not asked to complete one anyone considering Management roles should go out of their way and aim for an edge over their competition, what better way to do this than to provide detailed and specific market analysis for that business.
Common Mistakes
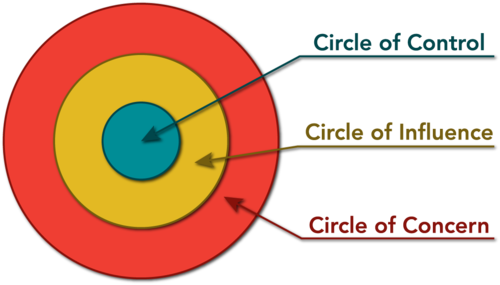
- One typical mistake that people make when completing a SWOT is looking in detail/depth at something that falls outside of the their "Circle of Control or Influence" - For example stating that the brand name isn't great, or the restaurant is poorly located inside the store - these are things that do not fall within a typical store managers control or influence, they should not be focussed on. Better to focus on something that as the newly hired manager, you could use your skills, strengths and abilities to control, influence and therefore naturally - Improve!
- Not being negative (constructively) - Candidates often use SWOT as an opportunity to tell their prospective employer how wonderful they are... this is not what it is for! You are likely to be speaking with a senior manager who will already be aware of the faults within a specific location (maybe that is why they are hiring a new manager.... ?) - If the potential candidate is not able to demonstrate their competency, capability and industry experience through the SWOT, they are giving themselves an uphill battle in the interview. It is imperative to highlight issues you see, however, this must be done whilst factoring in the circles of influence advice above and done constructively.
- Take a spare copy! Especially if your analysis is long, make sure you take a spare copy, so that you can leave it behind. It may be that you don't get a chance to read through the whole thing during the interview, so essential to take a spare copy to leave behind.